

This is an issue in networks with multiple equal-cost paths because under normal circumstances the packets that are generated by a networking device use the IP address from the outbound interface as the source address for the packets and because in a network with two or more equal-cost paths from the networking device to the receiving host each packet might use a different outbound interface. This address can be configured as the source address when the networking device needs to send data for protocols such as NetFlow or Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to another device in your network and you want the receiving device to always see the same source IP address from the networking device.
VIRTUAL LOOPBACK CABLE SOFTWARE
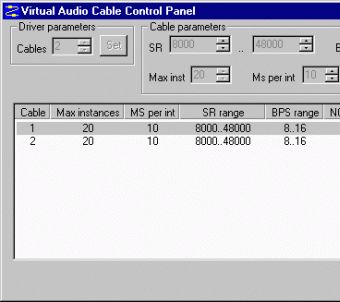
The ID is unique per virtual interface type to make the entire name string unique for example both a loopback 0 interface and a null 0 interface can exist, but two loopback 0 interfaces cannot exist in a single networking device.Ĭisco IOS software supports four types of virtual interfaces For example: loopback 0, tunnel 1, and fastethernet 0/0.1. You identify an individual virtual interface using a numerical ID after the virtual interface name.

Virtual interfaces exist only in software there are no physical elements. Physical interfaces have some form of physical element-for example, an RJ-45 male connector on an Ethernet cable. Virtual interfaces are network interfaces that are not associated with a physical interface. Loopback Interfaces Versus Loopback Mode.To configure virtual interfaces, you should understand the following concepts: Information About Configuring Virtual Interfaces Feature Information for Configuring Virtual Interfaces Prerequisites for Configuring Virtual Interfacesīefore virtual interfaces can be used in your network, you must have some physical (hardware) interfaces configured and be able to communicate between the networking devices on which you wish to use virtual interfaces.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
